T: +86-13715643479
E: contact@jqx-electric.com
E: contact@jqx-electric.com
(Huangwan Industrial Zone, Bianji Location) No.26, Zhouyuanzu Street, Hetang Town, Pengjiang District, Jiangmen City Guangdong Province, China
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-26 Origin: Site









You might wonder how long your incandescent bulb will last. On average, a standard incandescent bulb shines for about 1,000 hours. If you use it for 5 hours each day, you can expect it to last around 6 to 7 months. The actual time can change based on the type of incandescent bulb and how you use it. Knowing the expected lifespan helps you plan for replacements and manage your lighting costs at home or work.
Standard incandescent bulbs last about 1,000 to 1,200 hours, which means you may need to replace them every 6 to 7 months if used 5 hours daily.
Long-life incandescent bulbs can last up to 2,500 hours but may produce slightly less light than standard bulbs.
Turning lights off when not needed saves energy and helps bulbs last longer despite the small wear from switching them on and off.
Voltage changes and frequent switching cause stress to the bulb’s filament, which shortens its lifespan.
High temperatures and poor airflow around bulbs make filaments wear out faster, so use bulbs in cool, well-ventilated areas.
Wattage does not greatly affect incandescent bulb lifespan, but higher wattage bulbs use more energy and produce more heat.
LED bulbs last much longer and use less energy than incandescent bulbs, making them a cost-effective and efficient choice.
Proper installation, careful handling, and regular cleaning of fixtures help maximize the life of your incandescent bulbs.

When you use an incandescent bulb, you can expect a typical range for its lifespan. Most standard bulbs last between 1,000 and 1,200 hours. This number represents the average rated life, which means that half of a group of bulbs will burn out before reaching this point, and half will last longer. The average lifespan gives you a good idea of when you might need to replace your bulbs.
Note: The average rated life of an incandescent bulb depends on how you use it and the conditions in your home or business.
Some incandescent bulbs carry a "long-life" label. These bulbs use a thicker filament or special gas inside the glass to slow down wear. You might see long-life bulbs with an average rated life of up to 2,000 hours or more. While these bulbs last longer, they sometimes produce a little less light compared to standard bulbs.
| Bulb Type | Average Rated Life (hours) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 1,000 – 1,200 | Everyday lighting |
| Long-Life | 1,500 – 2,500 | Hard-to-reach fixtures |
| Specialty | 2,000+ | Decorative or specialty |
How you use your incandescent bulb affects its lifespan. If you turn on a bulb for 3 hours each day, it will last about a year. If you use it for 5 hours daily, you can expect it to last around 6 to 7 months. You can use this simple formula to estimate how long your bulb will last:
Estimated Lifespan (days) = Average Rated Life (hours) ÷ Hours Used Per Day
For example, if your bulb has an average rated life of 1,200 hours and you use it 4 hours a day:
1,200 ÷ 4 = 300 days (about 10 months)
If you leave your incandescent bulb on all the time, the lifespan will shorten. Running a bulb 24 hours a day means it will last only about 40 to 50 days. The constant heat wears out the filament faster. You should consider this if you need lighting that stays on for long periods.
Tip: Turning off lights when not needed helps you save energy and extends the average lifespan of your bulbs.
Voltage plays a big role in how long your incandescent bulb lasts. When the voltage in your home or business goes up and down, your bulbs experience stress. You might notice the light flickering when this happens. Flicker not only bothers your eyes but also signals that the bulb is under electrical stress. Here are some ways voltage fluctuations affect your bulbs:
Voltage fluctuations cause the light to flicker, which can be annoying and distracting.
These changes in voltage put extra stress on the bulb’s filament, wearing it out faster.
Over time, the service life of your bulb drops, and you may need to replace it sooner.
If your bulbs face high voltage or frequent voltage changes for a long time, their lifespan gets even shorter, which can lead to more frequent purchases and higher costs.
To get the most from your bulbs, try to keep your electrical system stable. If you notice frequent flickering, you might want to have an electrician check your wiring or voltage supply.
How often you turn your incandescent bulb on and off also affects its average rated life. Each time you flip the switch, the filament inside the bulb heats up very quickly. This sudden change in temperature is called thermal shock. The filament faces a strong surge of electricity—much higher than what it gets during normal use. Over time, this repeated heating and cooling weakens the filament, making it more likely to break. You can think of the filament like a rubber band that gets weaker every time you stretch it. The more you switch the bulb on and off, the sooner it will fail.
Even though frequent switching can shorten the bulb’s lifespan, the U.S. Department of Energy still recommends turning off incandescent bulbs when you do not need them. The energy savings outweigh the small reduction in life from switching.
The temperature around your bulb also matters. If you use your incandescent bulb in a hot room or a fixture that does not let heat escape, the filament will wear out faster. High temperatures speed up the evaporation of the tungsten filament, which shortens the bulb’s life. On the other hand, very cold temperatures can cause the filament to cool too quickly after you turn the bulb off. This rapid cooling can make the filament brittle and more likely to crack. For the best results, use your bulbs in places with moderate temperatures and good airflow. This helps you get the most out of each bulb and keeps your lighting reliable.
When you choose an incandescent bulb, you often look at the wattage. Wattage tells you how much energy the bulb uses. Many people think that a higher wattage means a longer or shorter lifespan. In reality, the relationship between wattage and lifespan is not always direct.
Most standard incandescent bulbs, whether they are 40 watts or 100 watts, have a typical lifespan of about 1,000 hours. This means that a 40-watt bulb and a 100-watt bulb will usually last about the same amount of time. The main difference is that the 100-watt bulb uses more electricity and produces more light.
Note: Higher wattage bulbs generate more heat. This extra heat can put more stress on the filament inside the bulb. Over time, this stress may cause the filament to burn out a little faster, but the rated lifespan for most standard bulbs remains close to 1,000 hours.
Here is a table that shows how wattage and lifespan compare for different types of bulbs:
| Bulb Type | Typical Wattage (Incandescent Equivalent) | Typical Lifespan (hours) | Notes on Lifespan and Wattage Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Incandescent | 40W to 150W | ~1,000 (standard) | Lifespan generally fixed around 1,000 hours |
| Halogen Incandescent | 29W to 72W (equivalent to 40W-100W inc.) | ~1,000 (standard), up to 3,000 (extended-life) | Extended-life versions last longer, not directly linked to wattage |
| CFL | 9-52W | ~10,000 | Lifespan much longer, wattage less important |
| LED | 6-20W | 10,000 to 25,000 | Longest lifespan, wattage less relevant than lumens |
You might notice that for incandescent bulbs, the lifespan does not change much with wattage. However, as you move to other types of bulbs, such as CFLs and LEDs, wattage becomes less important. These newer bulbs use less energy and last much longer.
Today, you should pay more attention to lumens instead of wattage. Lumens measure the amount of light a bulb produces. A 60-watt incandescent bulb gives off about 800 lumens. If you want the same brightness from an LED, you only need about 8 to 12 watts.
Key Points to Remember:
Standard incandescent bulbs, no matter the wattage, usually last about 1,000 hours.
Higher wattage bulbs use more energy and create more heat, but their lifespan is not much different from lower wattage bulbs.
For modern lighting, look at lumens to compare brightness, not just wattage.
By understanding how wattage affects your bulb, you can make better choices for your home or business lighting. Always check both the wattage and the lumens to get the right balance of brightness and efficiency.

When you compare an incandescent bulb to an LED light bulb, you see big differences in both lifespan and efficiency. An incandescent bulb usually lasts about 1,200 hours. An LED light bulb can shine for up to 25,000 hours. This means you would need to replace many incandescent bulbs before you need to change one LED bulb.
LEDs also use much less energy. To get the same brightness as a 60-watt incandescent, you only need a 7-watt LED. This saves you money on your electric bill. Over time, the total cost of using LEDs is much lower. You spend less on both bulbs and electricity.
Here is a table that shows how these light bulbs compare over 20 years:
| Aspect | Incandescent Bulb | CFL Bulb | LED Bulb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wattage for equivalent brightness | 60W | 14W | 7W |
| Average cost per bulb | $1 | $2 | $4 or less |
| Average lifespan | 1,200 hours | 8,000 hours | 25,000 hours |
| Number of bulbs needed for 25,000 hours | 21 | 3 | 1 |
| Total bulb purchase cost over 20 years | $21 | $6 | $4 |
| Electricity cost for 25,000 hours at $0.15/kWh | $169 | $52 | $30 |
| Total estimated cost over 20 years (bulbs + electricity) | $211 | $54 | $34 |
You can also see the cost difference in this chart:
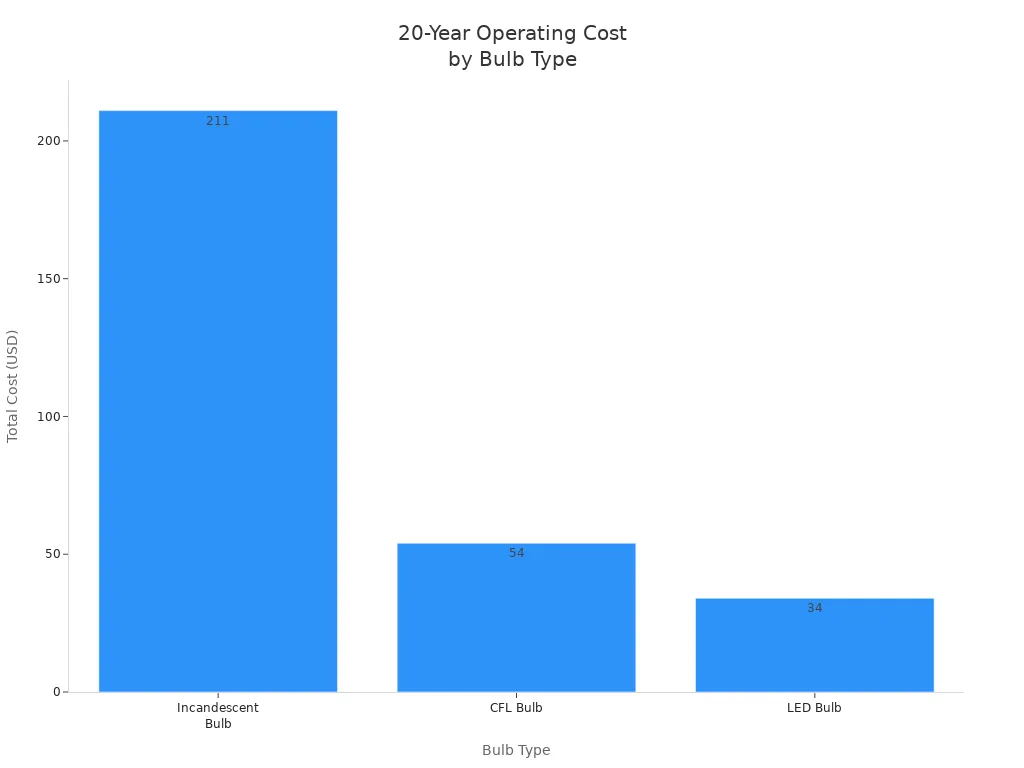
Tip: If you want to save money and change bulbs less often, LEDs are a smart choice.
CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp) bulbs offer another option for your home or business. A CFL light bulb lasts about 8,000 hours. This is much longer than the average rated life for various types of bulbs in the incandescent family. CFLs also use less energy. For the same brightness, a CFL uses about 14 watts, while an incandescent uses 60 watts.
CFLs cost a bit more to buy, but you save money over time because you buy fewer bulbs and use less electricity. You also help the environment by using less energy. However, CFLs contain a small amount of mercury, so you need to dispose of them properly.
Some specialty incandescent bulbs can last longer than standard ones. These bulbs may use a thicker filament or special gases to slow down wear. You might find specialty bulbs with lifespans of 2,000 hours or more. People often use them in places where changing a light bulb is hard, such as high ceilings or outdoor fixtures.
Keep in mind, specialty bulbs may not be as bright or efficient as LEDs or CFLs. They work well for decorative lighting or unique fixtures. If you want the longest life and best efficiency, LEDs still lead the way.
Proper installation helps you get the best performance from your incandescent bulbs. Always handle bulbs with clean, dry hands. Oils from your skin can create hot spots on the glass, which may cause the bulb to fail early. Make sure the bulb fits snugly in the socket. A loose connection can cause flickering and shorten the bulb’s life. Use the correct wattage for your fixture. If you use a bulb with higher wattage than recommended, you risk overheating the fixture and the bulb. This can lead to a shorter lifespan.
Tip: Before installing a new bulb, turn off the power to the fixture. This keeps you safe and prevents electrical surges that can damage the bulb.
Your daily habits play a big role in how long your bulbs last. Try to avoid turning lights on and off too often. Each time you switch a bulb on, the filament faces a surge of electricity. This surge can weaken the filament over time. If you know you will leave a room for just a few minutes, you might leave the light on. For longer absences, turn it off to save energy. Use dimmer switches if your bulbs support them. Dimming reduces the stress on the filament and can help prolong light bulb lifespan.
You can also group your lighting. Use task lighting for activities like reading or cooking, and keep general lighting off when not needed. This approach reduces the total hours your bulbs operate, which helps them last longer.
The environment around your bulbs affects their performance. Keep bulbs in areas with good airflow. Heat builds up in closed fixtures and can cause the filament to burn out faster. Avoid using incandescent bulbs in places with high humidity, such as bathrooms or outdoor fixtures without proper protection. Moisture can damage the bulb and socket. If you use bulbs in cold areas, let them cool down slowly after turning them off. Sudden temperature changes can crack the filament.
Dust and dirt can also trap heat around the bulb. Clean your fixtures regularly to prevent buildup. This simple step helps maintain a stable temperature and supports a longer bulb lifespan.
️ Note: Small changes in installation, usage, and environment can make a big difference. By following these tips, you can maximize the value of your bulbs and reduce how often you need to replace them.
You can spot the signs that your incandescent bulb needs replacing. The most obvious sign is when the bulb stops lighting up. Sometimes, you may notice the filament inside the bulb has broken or turned black. If the bulb flickers often or gives off a dimmer light than usual, it may be close to the end of its life.
You should also check bulbs in hard-to-reach places regularly. If you use bulbs in stairwells, high ceilings, or outdoor fixtures, plan to replace them before they burn out completely. This helps you avoid sudden darkness in important areas.
Here are some tips to help you decide when to replace your incandescent bulbs:
Replace bulbs that flicker or dim, even if they still work.
Swap out bulbs in safety-critical areas before they fail.
Keep track of how many hours you use each bulb. If you use a bulb for about 5 hours a day, expect to replace it every 6 to 7 months.
Consider replacing all bulbs in a group at the same time. This saves you time and keeps your lighting consistent.
Tip: Write the installation date on the bulb base with a marker. This makes it easy to know when to expect a replacement.
When you replace an incandescent bulb, you need to dispose of it safely. Incandescent bulbs do not contain hazardous materials like mercury, so you can throw them away with regular household trash in most areas. However, you should always wrap the bulb in paper or place it in a sturdy bag before tossing it out. This prevents broken glass from causing injuries.
You may wonder how incandescent bulbs compare to other types when it comes to disposal. Here is a quick overview:
Incandescent bulbs do not contain mercury or other toxic substances.
CFLs and fluorescent bulbs contain small amounts of mercury. If these bulbs break or end up in landfills, mercury can escape into the air or water, which can harm people and wildlife.
You must recycle CFLs and other mercury-containing bulbs at special collection sites or through retailer take-back programs.
Incandescent bulbs are not classified as hazardous waste for households, so you do not need to follow special disposal rules.
Businesses and institutions must follow specific regulations for disposing of mercury-containing bulbs.
♻️ Note: Even though incandescent bulbs are safe to throw away, recycling programs may accept them for glass and metal recovery. Check with your local waste management service for recycling options.
If you handle CFLs or other energy-efficient bulbs, store used bulbs in sturdy cartons to prevent breakage. Always follow local guidelines for safe disposal or recycling. By handling all bulbs with care, you help protect your family and the environment.
When you choose a light bulb, you want to know what makes each type different. Incandescent bulbs have been around for a long time. Many people like them because they are simple and familiar. You can see their main advantages and disadvantages in the table below:
| Aspect | Advantages of Incandescent Bulbs | Disadvantages of Incandescent Bulbs |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low initial cost due to simple design and long manufacturing history | Energy inefficient: most power is lost as heat, leading to high electricity bills |
| Light Output | Relatively high light output based on filament heat | Very short lifespan (~1,000 hours) compared to LEDs (up to 50,000 hours) |
| Dimmability | Can be dimmed using rheostats | Produces significant heat, which may require room cooling, increasing energy costs |
| Use in Cold Weather | Heat produced can provide warmth in cold environments | Heat production is a disadvantage in warm environments |
| Overall Comparison | Simple, cheap, and familiar technology | Outdated technology with many disadvantages compared to LEDs, which are more energy-efficient, durable, and eco-friendly |
You might like incandescent bulbs for their warm light and low price. You can use them with most dimmer switches. However, they do not last as long as other options. They also use more electricity, which can raise your energy bills. The heat they produce can be helpful in cold rooms, but it can be a problem in warmer spaces.
Tip: Think about where you use your bulbs. If you need a bulb for a place that is hard to reach, a longer-lasting option may save you time and effort.
You have more choices than ever when you shop for a new light bulb. Many people now pick LED bulbs or CFLs because they last longer and use less energy. LEDs can shine for up to 25,000 hours. CFLs often last about 8,000 hours. Both types use much less electricity than traditional bulbs.
Some countries have rules about which bulbs you can buy. For example, the United States set efficiency standards for general-service bulbs. Canada and Australia also have bans on many types of incandescent bulbs. Specialty bulbs, like those for ovens or decorative fixtures, are often still allowed. Here is a quick look at some regulations:
| Region | Regulation / Law | Key Provisions and Dates | Exemptions / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 (EISA) | Set efficiency standards for general-service bulbs (310–2600 lumens), effective 2012; second tier by 2020 requiring 45 lumens/watt | Specialty bulbs exempt (appliance lamps, rough service, 3-way, colored, stage lighting, etc.) |
| Canada | Federal ban on import and sale of incandescent bulbs | 75- and 100-watt bulbs banned from Jan 1, 2014; 40- and 60-watt banned from Jan 1, 2015 | Exemptions for oven lights, decorative lamps, appliance bulbs, 3-way fixtures, chandeliers, rough service bulbs |
| Australia | Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) | Non-compliant incandescent bulbs banned from retail sale by November 2009; imports banned from November 2008 | High-efficiency halogen bulbs meeting standards allowed |
When you upgrade, you get more than just a longer-lasting bulb. You also save money on your electric bill. LEDs and CFLs come in many shapes and colors. You can find one for almost any fixture in your home or business.
Note: Always check the packaging for brightness (lumens) and color temperature. This helps you pick the right light for your needs.
You now know that the typical lifespan of an incandescent bulb ranges from 750 to 2,000 hours. Factors like voltage, temperature, and switching habits can shorten or extend this time. When you compare incandescent bulbs to CFLs, you see clear differences:
| Attribute | Incandescent Bulb | CFL Bulb |
|---|---|---|
| Average Lifespan | 750–2,000 hours | 8,000–15,000 hours |
| Energy Use | High | Low |
To get the most from your bulbs, install them correctly, avoid frequent switching, and keep fixtures clean.
You may notice the bulb flickering, dimming, or making a faint buzzing sound. Sometimes, the filament inside looks broken or darkened. Replace the bulb soon to avoid sudden darkness.
Yes, you can use most incandescent bulbs with standard dimmer switches. Dimming the light can help extend the bulb’s lifespan and save energy.
Yes, leaving a bulb on for long hours causes the filament to wear out faster. You will need to replace the bulb more often if you keep it on all night.
Long-life bulbs use thicker filaments or special gases. These features slow down filament wear. Specialty bulbs also last longer because of their unique design.
Avoid touching bulbs with bare hands. Oils from your skin can create hot spots on the glass. These spots may cause the bulb to fail early.
Most recycling programs do not accept incandescent bulbs. You can throw them away with regular trash. Wrap the bulb in paper or a bag to prevent injury from broken glass.
Check the fixture’s label for the maximum wattage. Never use a bulb with higher wattage than recommended. Using the correct wattage keeps your bulb and fixture safe.